Describe the Three Levels of Cache Used by a Processor
A primary cache is always located on the processor chip. Cache memory within a computer is classified under various types depending upon its physical location within the computer whether they are.

Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times
The more cache there is the more data can be stored closer to the CPU.
. The Levels of CPU Cache Memory. Techopedia Explains Level 3 Cache L3 Cache The L3 cache is usually built onto the motherboard between the main memory RAM and the L1 and L2 caches of the processor module. It allows the CPU to keep operating at peak performance without idling as it provides very fast transfer rates compared to other types of memory.
Often the Level 2 cache is also housed on the processor chip. Earlier L2 cache designs placed them on the motherboard which made them quite slow. CPU Cache memory is divided into three levels.
L2 cache or secondary cache is often more capacious than L1. Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2 cache. A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit CPU of a computer to reduce the average cost time or energy to access data from the main memory.
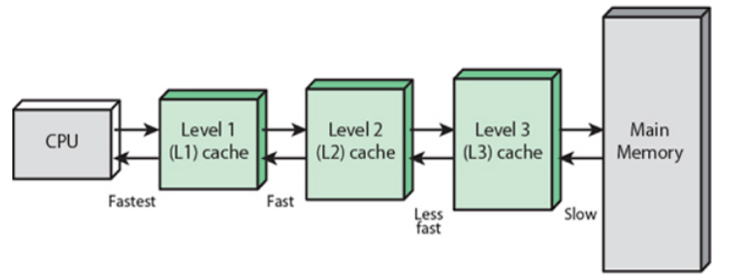
Cache is graded as Level 1 L1 Level 2 L2 and Level 3 L3. Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2 cache. L1 L2 and L3.
This cache is small and its access time is comparable to that of processor registers. Level 1 L1 or Registers It stores and accepts the data which is immediately stores in the CPU. It is used with the processor to facilitate the access of data from the systems main memory or RAM.
It is referred to as the level 2 L2 cache. It is used to hold data and instructions that. Memory further from the processor core then L2 cache but still within the processor housing.
Memory on the processor chip is called level 1 cache. There are three general cache levels. L1 cache or primary cache is extremely fast but relatively small and is usually embedded in the processor chip as CPU cache.
Secondary Cache Secondary cache is placed between the primary cache and the rest of the memory. Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache. For example instruction register program counter accumulator.
L1 is the fastest and has the least amount of storage while L2 and L3 become slower but have higher storing capacity. This serves as another bridge to park information like processor commands and frequently used data in order to prevent bottlenecks resulting from the fetching of these data. The processor cache typically consists of two levels which are the L1 cache and the L2 cache.
There are three types of Cache as L1 L2 and L3. Some processors use a third cache farther from the processor core but still in the processor package which is called Level 3 cache L3 cache. In a fully associative cache every memory location can be cached in any cache line.
A level 2 cache L2 cache is a CPU cache memory that is located outside and separate from the microprocessor chip core although it is found on the same processor chip package. Memory on the processor die 2. There is three types of cache.
Located between the processor and main memory Secondary Cache L2 3. Some processors use a third cache farther from the processor core but still in the processor package which is called Level 3 cache L3 cache. There are multiple different kinds of cache memory levels as follows Level 1 L1 or Registers It is a type of memory in which data is stored and accepted that are immediately stored in the CPU.
Levels of Cache Memory There can be various levels of cache memory they are as follows. In multi-core CPUs a separate L1 cache is available for each core. L1 is usually part of the CPU chip itself and is both the.
Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2 cache. The processor uses L1 cache to hold the most frequently used instructions and data. Every modern processor comes with a dedicated cache that holds processor instructions and data meant for almost immediate use.
The memory hierarchy is again according to the speed and thus the size of the cache. Describe the three levels of cache used by a processor. L1 Level 1 cache is the fastest memory that is present in a computer system.
A cache is a smaller faster memory located closer to a processor core which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locationsMost CPUs have a hierarchy of multiple cache levels. The Processor Cache is memory that store data code commands etc. 1 2 3.
The term cache hit means the data or instruction processor need is in cache cache miss in the opposite situation. Generally the L1 cache is the smallest in size and built into the processor chip. Cache is a component in the computer that stores data so that future requests for the data can be served faster.
L1 cache is die L2 cache is off the die L3 cache is shared What can a DIMM use to hold data and amplify a signal just before the data is written to the module. Memory within the processor housing but not on the processor die 3. L1 Level 1 Cache 2KB - 64KB - is small in comparison to others making it faster than the restL2 Level 2 Cache 256KB - 512KB - is a slightly larger therefore accompanied by some latencyL3 Level 3 Cache 1MB -8MB - is the largest among all the cache levels even though it is slower it is still faster than the RAM.
Some processors use a third cache farther from the processor core but still in the processor package which is called Level 3 cache L3 cache. This is referred to as the first level cache. So does the CPU cache size make a difference to performance.
Processor Cache reduces the average time to access memory. Examples of L1 cache are. The difference between L1 L2 and L3 cache is that the L1 cache is the fastest cache and L3 cache is the slowest cache while the L2 cache is slower than L1 but faster than L3 cache.
Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache. L1 L2 and L3. Cache currently comes in three levels L1 L2 and L3.
Part of the processor chip Primary Cache L1 2. External to the processor Main Memory L3. Parity A DDR4 DIMM running at a speed of 2666 MHz has what PC rating.
Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache. L2 cache is bigger in capacity than L1 cache but slower in speed.
Cache Memory And Its Different Levels
What Limits The Levels Of Cache Why Are There Only Two Or Three Levels Of Cache Quora

No comments for "Describe the Three Levels of Cache Used by a Processor"
Post a Comment